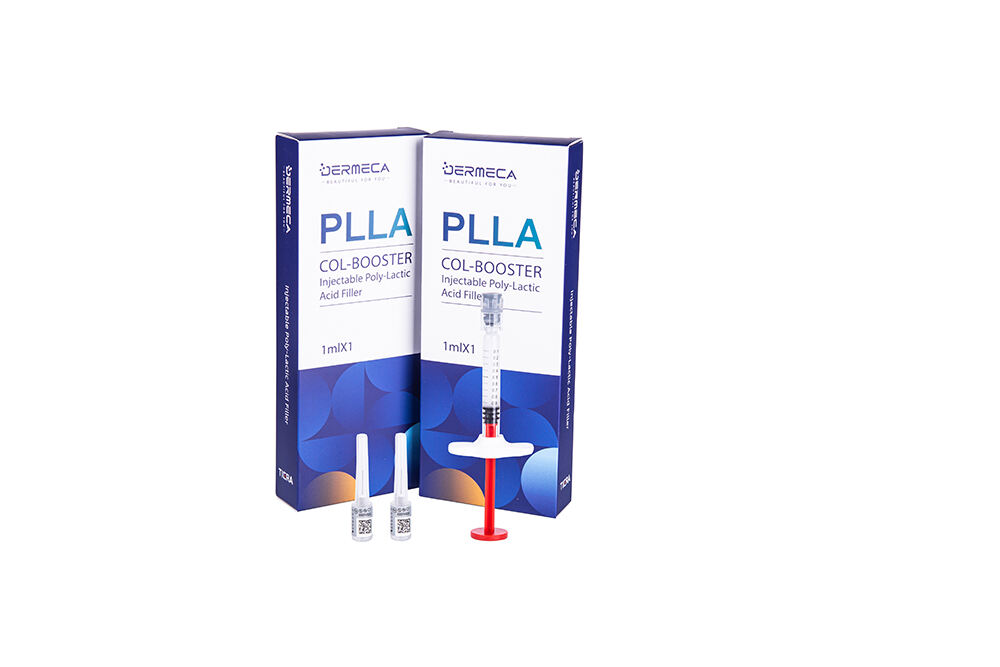
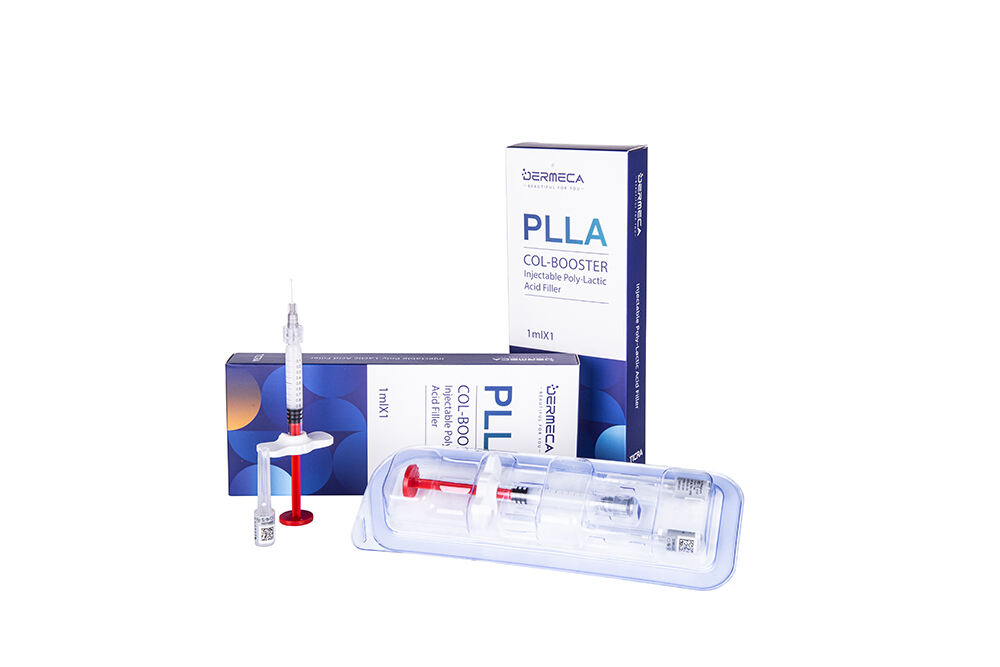
Dermeca Plla Filler 1ml , Collagen Stimulator
Name: Dermeca Lido Injectable Plla Filler
Attribute: Injectable facial implant
PLLA-b-PEG microsphere : 150mg/ml
HA Concentration: 17mg/ml
Lidocaine : 0.3mg/ml
- Overview
Dermeca Plla Filler, a formulation of cross-linked hyaluronic acid sodium gel infusedwith PLLA microspheres, is meticulously crafted for targeted injections to areas that seekvolumetric enhancement and lifting effects. lt is ideal for facial zones such as the temporalareas, brow ridge, nasal structure, columella nasi, chin region, base of the nose, and the deepmalar muscle, offering a subtle and rejuvenating lift, This treatment is engineered to deliver aresult that appears both natural and restorative of youthful contours.
Dermeca Plla Filler consists of a prefilled syringe, a sterile hypodermic needle for single use, and the gel prefilled in the syringe. The gel is mainly composed of cross-linked sodium hyaluronate, poly-l-lactic acid (PLLA) microspheres (labeled content: 18%), lidocaine hydrochloride, and the phosphate buffer system. The nominal concentrations of sodium hyaluronate (prepared by microbial fermentation) and lidocaine hydrochloride are 17 mg/mL and 3 mg/mL, respectively. The syringe prefilled with gel is sterilized by autoclaving, and the sterile hypodermic needle for single use is sterilized by ethylene oxide or irradiation. The filler is for single use (shelf life: 2 years).
The filler is a milky white viscous gel, with cross-linked sodium hyaluronate and PLLA microspheres as the main components. The median particle size of PLLA microspheres is 32 μm ± 6 μm, with more than 95% of the microspheres being 20–45 μm in size. The gel is a dermal tissue filler, which is injected into the deep layers of the dermis and the subcutaneous superficial and deep layers to correct the nasolabial folds, and the PLLA microspheres contained in the gel can prolong the filling duration. The Wrinkle Severity Rating Scale (WSRS) score in most subjects with improvement is still greater than 1 point at 12 months post-surgery.
| Name | Dermeca Lido Injectable Plla Filler |
| Attribute | Injectable facial implant |
| HA Concentration | 17mg/ml |
| PLLA-b-PEG microsphere | 150mg/ml |
| Lidocaine | 0.3mg/ml |
| Version | Lidocaine |
| Injection Zone | Face |
| Effect Duration | Up to 2 years |
| Storage Condition | Store at 2°C–25°C, and do not freeze |
| Indications for use | The gel is indicated for injection into the deep layers of the dermis and the subcutaneous superficial and deep layers to correct moderate to severe nasolabial folds. |
Contraindications
• Early-onset or active autoimmune diseases, on treatment with immunosuppressive or modulating agents, active skin infection.
• Herpes.
• Allergy to hyaluronic acid, poly-l-lactic acid, lactic acid, polyethylene glycol, or lidocaine (local anesthetic).
• Abnormal coagulation mechanisms; treated with thrombus-dissolving agents, anticoagulants, or platelet coagulation inhibitors within two weeks before injection.
• Pregnant/lactating women and minors.
• Keloid/hypertrophic scar constitution.
PRECAUTIONS
• Before using the product, physicians must carefully read the IFU to understand the product features and related injection risks. Physicians are expected to counsel the patient and discuss the potential benefits and risks of treatment.
• The procedure of injection therapy itself carries a risk of infection. Therefore, routine precautions related to injection therapy should be followed. Prior to the injection, local disinfection should be carried out; during the injection, the aseptic operation regulations on surgical treatment must be strictly followed.
• For patients taking drugs that affect platelet function, injection may cause bruising or bleeding at the injection site.
• The efficacy and retention time of the gel are affected by the nature of the defect, the degree of correction, the depth of injection, the injection technique of the physician, and the individual constitution. Gel use in excess may cause the risk of swelling, and overcorrection should be avoided.
• Inflammatory reaction may be caused by laser treatment, chemical peeling, or any other treatment that may cause skin irritation after or before gel injection. If the patient has received the above treatment, it should be determined by a professional physician that the skin is completely healed before gel injection. The above treatment should be received with confirmation by a professional physician 1 month after gel injection.
• After the injection is completed, the injection site should not be exposed to intense heat (such as sunbathing) or extreme cold environments within 7 days. The patient should avoid consuming irritating medications or foods. The patient should not receive skincare treatments such as massages and facials at will; if such treatments are necessary, the patient should consult a professional physician.
• The degradation period of the L-lactic acid-ethylene glycol copolymer microspheres contained in the gel is relatively long. Therefore, apart from improper or excessive injections, there are still risks of subcutaneous nodules, redness, and chronic granulomatous disease (CGD) at the injection site even with normal injections.
• The injection of the gel into the human body rarely causes microsphere dispersion or displacement. The microspheres contained in the gel are difficult to remove directly by surgical incision. If local tissue swelling, induration, or CGD occurs due to microsphere dispersion or displacement, topical or oral corticosteroids and local anti-inflammatory treatments can be administered. If necessary, the lesions can be surgically removed along with the microspheres.
• Except for correcting nasolabial folds, the product is not suitable for use on other areas as the safety and efficacy have not been established.
• Except for the deep layers of the dermis and the subcutaneous superficial and deep layers, the product is not suitable for use on other layers as the safety and efficacy have not been established.
• The safety and efficacy of multiple injections of the gel have not been established.
• The safety and efficacy of the gel in pregnant/lactating women, minors, and elderly people over 65 years old have not been established. It is recommended that the gel should be used in the population aged 18–65 years.
• The safety and efficacy of the gel in combination with other drugs and devices have not been established.
• The product should be disposed of as medical waste after use or beyond the expiration date.
EXPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS
A local, short-term, injection-related reaction may occur after gel injection. Possible reactions mainly include redness, bruising, pain, swelling, and pruritus at the injection site. These reactions typically occur on the day of injection or within 3–5 days after injection, and usually improve spontaneously after about 1–4 weeks. Usually, only simple remedies like ice compress are sufficient. If symptoms are severe, consulting a physician for appropriate clinical treatment based on the severity is recommended.
RARE ADVERSE REACTIONS
• Skin depigmentation at the injection site may be caused by lidocaine inducing local capillary constriction.
• Some patients may develop induration or small nodules at the injection site, which are related to the injection technique and can be either acute (within 1 month after injection) or delayed (several months after injection). Small nodules usually resolve spontaneously. For severe nodules, topical corticosteroids can be applied for treatment. Larger nodules or those resistant to medication may require surgical removal, which should be consulted with a physician.
• Some patients may experience short-term allergic reactions, such as localized erythema, mild swelling, and pruritus. In severe cases, it may result in localized papules or wheals. Patients may consult a physician for topical or oral corticosteroids in combination with physical treatments like ice compress. If necessary, immunogen screening can be performed to prevent future allergic reactions.
• Some patients may experience infection at the implant site in the short or long term. Consult a physician for regular anti-infection treatment and consider drainage by incision if necessary.
• Some patients may experience acute or chronic severe local inflammatory reactions, skin pigmentation, etc. Consult a physician for anti-inflammatory and antihistamine treatment. After the inflammatory active stage ends, consider receiving other related treatments to remove pigmentation.
• No adverse reactions including granuloma, epidermal necrosis, and urticaria have been reported in clinical trials of the product; if present, these adverse reactions can be relieved by applying topical or oral corticosteroids for several weeks to months. The product should not be used in patients who have experienced similar adverse reactions.
• The adverse reaction of vascular embolism has not been reported in the clinical trials of the product. If the gel is mistakenly injected into a blood vessel due to improper operation, and the patient experiences any of the following symptoms including changes in vision, whitening of the skin in the affected area, or abnormal pain, the injection should be stopped immediately. If the patient experiences the above symptoms after injection, he/she should seek immediate medical treatment. Injecting hyaluronidase locally can be used to dissolve the sodium hyaluronate gel. For the removal of microspheres, a comprehensive therapeutic approach can be adopted, including vasodilation promotion, skin wound management, nutrition, and anti-inflammatory treatment. This may involve local heat compress, the use of vasodilators like nitroglycerin, topical antibiotic application or systemic antibiotic administration, and the use of topical or oral corticosteroids for treatment.